Introduction to SPAN, RSPAN and ERSPAN
Switch port
Analyzer (SPAN)
It is an high efficient traffic monitoring protocol and used
to duplicated network traffic to one or more monitor interfaces as it
transverse the switch. SPAN is used for network troubleshooting connectivity problems
and measuring network utilization and performance.
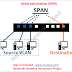
In the case if SPAN only, the port will get the mirrors
traffic from one or more interface on the switch to one or more interfaces on
the same switch which means there is a source port whose traffic needs to be
monitored and will mirror the full traffic information on the alternate port
which will be called as SPAN port.
Fig 1.1- SPAN
|
Basic Configuration for SPAN Port with Source and Destination ports
RouteXP_SW1#
configure terminal
RouteXP_SW1
(config)# monitor session 1 source interface Fa0/21
RouteXP_SW1
(config)# monitor session 1 destination interface Fa0/11
RouteXP_SW1
(config)#end
Remote SPAN
(RSPAN):
Similarly SPAN, we have the other kind of the SPAN protocol
called as Remote SPAN. It is an extension of SPAN. RSPAN permits admin to
monitor traffic from source ports distributed over multiple switches, which
means that admin can monitor centrally network capture devices. RSPAN works by duplicating
or mirroring the traffic from the source ports of an RSPAN session onto a VLAN
that is precisely for the RSPAN session.
This VLAN is then trunked to other
switches, allowing the RSPAN session traffic to be transported across multiple
switches. On the switch that contains the destination port for the session,
traffic from the RSPAN session VLAN is simply mirrored out the destination
port.
In order to configure RSPAN you need to have an RSPAN VLAN, those VLANs have special properties and can’t be assigned to any access ports. To create a VLAN for RSPAN on Cisco IOS, you must create the VLAN via the config-vlan configuration mode, as opposed to using the older VLAN database configuration mode. During the process of defining VLAN parameters, you must specify that the new VLAN is an RSPAN VLAN by configuring the remote-span VLAN configuration command.
We will discuss the scenario with the configuration for RSPAN
Encapsulated
remote SPAN (ERSPAN):
Encapsulated Remote SPAN (ERSPAN), as the name says, offers
generic routing encapsulation (GRE) for all captured traffic and permits it to
be extended across Layer 3 domains.
ERSPAN is a basically a Cisco proprietary feature and is
available only to Catalyst 6500, 7600, Nexus, and ASR 1000 platforms to date.
The ASR 1000 supports ERSPAN source (monitoring) only on Fast Ethernet, Gigabit
Ethernet, and port-channel interfaces.
We will discuss the scenario with the configuration for ERSPAN