The Use of the Asymmetric routing
Today I am going to talk about the the concept of asymmetric routing and what is the purpose of the asymmetric routing in details. In simple words, Asymmetric routing is used when a packet takes one path to the destination and takes another path when returning to the source. It can be used of manual purposes where we want the sending and the receiving path will be different.
Asymmetric routing is common within most networks i.e. the larger the network, the more likely there is asymmetric routing in the network. Asymmetric routing is an undesirable situation for many network devices including, firewalls, VPNs, and Load Balancer appliances. These devices all rely on seeing every packet to function properly.
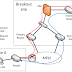
Below is the example showing the asymmetric routing where we have two different paths for sending and receiving the packets or you can say traffic flow path are different for sending and receiving the packets. In the below topology, you can see that Site A sending the traffic to internet via Primary Router and then to ASA and then to internet Router while receiving from Internet router then secondary router and then to Site A via MPLS cloud. So this is basically called as asymmetric routing.
 |
| Fig 1.1- Asymmetric Routing |
Asymmetric routing can occur in a smaller scale additionally. it can take place in a scenario in which an organisation makes use of distinct routes, like a VPN and a leased line, as an example, to their branch workplace. In complete Cluster generation context, we talk about uneven routing whilst we have a scenario in which segments on a single connection are available in to the community via one node and go out through any other node. underneath is the any other instance of asymmetric traffic.
Asymmetric routing is not a hassle via itself, however will motive troubles while community deal with Translation (NAT) or firewalls are used inside the routed route. for instance, in firewalls, country information is built whilst the packets waft from a better safety area to a lower protection area. The firewall will be an go out factor from one protection area to the other. If the return path passes through every other firewall, the packet will no longer be allowed to traverse the firewall from the lower to higher protection domain due to the fact the firewall within the go back path will no longer have any nation information. The nation statistics exists in the first firewall.
Make Your Routing Symmetric
This could appear clean, but in real network designs it is able to be a giant undertaking. Even still, you would be amazed to peer how many large networks use symmetric routing at certain elements of their network to permit nation-conscious safety gadgets to characteristic or to resolve other networking problems. this is particularly commonplace at net edges, where it isn't always unheard of to peer a whole connection to an ISP mendacity dormant while the primary connection handles all the load. every other example of uneven direction beneath.
 |
| Fig 1.2- Another Example of Asymmetric Routing |
Load Balance Per Flow Rather Than Per Packet
Most L3 devices may be configured to do considered one of two things while same-cost paths exist for a given network destination. within the first alternative, packets are simply balanced in round-robin layout, with every successive packet going to the subsequent to be had upstream router. this selection causes the most heartache with internal safety systems inclusive of IDS.
The second one, more preferred, choice is to load balance based totally on a given waft. this indicates visitors with a particular supply and vacation spot IP address and port (often called a four tuple) is continually sent by means of a selected upstream router. This lets in IDS systems and other nation-conscious gadgets to as a minimum see half of of the verbal exchange in a steady way. sadly, this does nothing to the return site visitors, which nonetheless may flow over a different link.
Use State-Sharing Security Devices
Because the hassle of asymmetric visitors manifests itself an increasing number of in networks, community safety carriers are beginning to offer alternatives permitting the kingdom records inside one protection tool to be shared with some other.
Firewalls 1 and 2 should alternate their nation table information to ensure that if the other tool sees a part of a given float, it's going to realize to allow the visitors. frequently, the quantity of records exchanged is great and calls for that devoted hyperlinks be configured between the firewalls to change the kingdom records.
Consider L2 Redundancy as a Workaround
With the careful introduction of L2 redundancy in preference to L3, technology such as digital Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) or warm Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) can permit traffic to glide through a single place at the same time as still providing redundancy. this feature works nice on excessive-velocity connections in which the use of handiest one direction in place of or greater does now not affect community overall performance.