Best Practices in the Enterprise or Campus Network Design
Today I am going to talk about the best practices in the Campus network design. I knew in the basic campus network architecture we have core, distribution and access layers. The campus access layer switching infrastructure must be resilient to attacks including direct, indirect, intentional, and unintentional types of attacks. In addition, they must offer protection to users and devices within the Layer 2 domain.
I am going to talk about best practices of the Campus Network where i talk about the VLAN best practices and the best practices of the switching Security.
 |
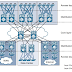
| Fig 1.1- Campus Network Architecture |
The key measures for providing switching security on the access switches include the following:
Switching Security
- Restrict broadcast domains
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Security—Implement Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+), BPDU Guard, and STP Root Guard to protect against inadvertent loops
- DHCP Protection—Implement DHCP snooping on access VLANs to protect against DHCP starvation and rogue DHCP server attacks
- IP Spoofing Protection—Implement IP Source Guard on access ports
- ARP Spoofing Protection—Implement dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) on access VLANs
- MAC Flooding Protection—Enable Port Security on access ports
- Broadcast and Multicast Storm Protection—Enable storm control on access ports
VLAN best Practices
- Restrict VLANs to a single switch
- Configure separate VLANs for voice and data
- Configure all user-facing ports as non-trunking (DTP off)
- Disable VLAN dynamic trunk negotiation trunking on user ports
- Explicitly configure trunking on infrastructure ports rather than auto negotiation
- Use VTP transparent mode
- Disable unused ports and place in unused VLAN
- Do not use VLAN 1 for anything
- Use all tagged mode for native VLAN on trunks